Nanomaterials refer to materials that have at least one dimension in the three-dimensional space in the nanoscale range (1-100 nm) or are composed of them as basic units, which is roughly equivalent to a scale in which 10 to 100 atoms are closely arranged together.
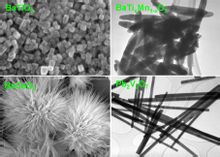
Composite oxide one-dimensional and zero-dimensional single crystal nanomaterials
In terms of size, the size of fine particles which usually produce a significant change in physicochemical properties is below 0.1 μm (Note 1 m = 100 cm, 1 cm = 10000 μm, 1 μm = 1000 nm, 1 nm = 10 Å), ie Below 100 nm. Therefore, particles with a particle size of 1 to 100 nm are called ultrafine particles and are also a nanomaterial.
Nano-metal materials were successfully developed in the mid-1980s. Later, nano-semiconductor films, nano-ceramics, nano-ceramic materials and nano-biomedical materials were introduced.
The nano-scale structural material is simply referred to as a nanometer material, and the size of the structural unit is between 1 nm and 100 nm. Since its size is close to the coherence length of electrons, its properties change greatly due to the self-organization caused by strong coherence. Moreover, its size is close to the wavelength of light, and its special effect with large surface, so its characteristics, such as melting point, magnetic properties, optical, thermal conductivity, conductive properties, etc., are often different from the overall state of the material. The nature of the performance.
Nanoparticle materials, also known as ultrafine particulate materials, consist of nanoparticles. Nanoparticles, also called ultrafine particles, generally refer to particles between 1 and 100 nm in size, which are transitional regions at the junction of clusters and macroscopic objects. Such systems are not typical from the microscopic and macroscopic perspectives. The microscopic system is also an atypical macroscopic system. It is a typical mesoscopic system with surface effects, small size effects and macroscopic quantum tunneling effects. When people subdivide macroscopic objects into ultrafine particles (nanoscale), it will show many singular characteristics, namely its

Rare earth nanomaterial
The optical, thermal, electrical, magnetic, mechanical, and chemical properties will be significantly different from those of bulk solids.
The broad scope of nanotechnology can include nanomaterial technology and nanofabrication technology, nanometer measurement technology, and nanometer application technology. Among them, nanomaterial technology focuses on the production of nano-functional materials (ultrafine powder, coating, nano-modified materials, etc.), performance testing techniques (chemical composition, microstructure, surface morphology, materials, chemicals, electricity, magnetism, heat and optics, etc.) performance). Nanofabrication technology includes precision machining technology (energy beam processing, etc.) and scanning probe technology.
Nanomaterials have certain uniqueness. When the material scale is small to a certain extent, it must be replaced by quantum mechanics instead of traditional mechanics to describe its behavior. When the particle size is reduced from 10 micrometers to 10 nanometers, the particle size Although it is changed to 1000 times, it will be 10 times as large as 9 times in terms of volume, so there will be a significant difference in behavior between the two.
The reason why nanoparticles are different from bulk materials is that their surface area is relatively increased, that is, the surface of the ultrafine particles is covered with a stepped structure, which represents unstable atoms with high surface energy. Such atoms are highly susceptible to adsorption bonding with foreign atoms and provide a large surface of active atoms due to particle size reduction.
As far as the melting point is concerned, in the nanopowder, since each particle has a small number of atoms, the surface atoms are in an unstable state, and the amplitude of the surface lattice vibration is large, so that the surface energy is high, resulting in the unique thermal properties of the ultrafine particles. That is, the melting point is lowered, and the nano powder is easily sintered at a lower temperature than the conventional powder, and becomes a good sintering promoting material.
Generally, the common magnetic substances belong to a collection of multi-magnetic regions. When the particle size is small enough to distinguish the magnetic regions, a magnetic substance of a single magnetic region is formed. Therefore, when the magnetic material is formed into ultrafine particles or a film, it becomes an excellent magnetic material.

 Company Profile
Changzhou NaO Technology Co.,Ltd. is located in the national high-tech innovation park - Changzhou Science and Education City, Jiangsu Province, and is a high-tech enterprise in Jiangsu Province.
Company Profile
Changzhou NaO Technology Co.,Ltd. is located in the national high-tech innovation park - Changzhou Science and Education City, Jiangsu Province, and is a high-tech enterprise in Jiangsu Province.
 Qualification honor
Our company has undertaken more than 10 national, provincial and municipal science and technology projects and applied for more than 80 invention patents. It is a high-tech enterprise in Jiangsu Province and a technological innovation enterprise in Jiangsu Province.
Qualification honor
Our company has undertaken more than 10 national, provincial and municipal science and technology projects and applied for more than 80 invention patents. It is a high-tech enterprise in Jiangsu Province and a technological innovation enterprise in Jiangsu Province.
 Company news
Company news, please click to enter。
Company news
Company news, please click to enter。
 Industry news
For the latest news in the industry, please click to enter。
Industry news
For the latest news in the industry, please click to enter。
 Message
You are welcome to browse our website. If you need help, please call our contact number, or click to enter the message platform to leave a message, we will reply you in the first time.
Message
You are welcome to browse our website. If you need help, please call our contact number, or click to enter the message platform to leave a message, we will reply you in the first time.
 Contact information
Contact: Landline: 0519-83277346
Mr. Yao: 13813572798
Mr. Wang: 18861101169
Contact information
Contact: Landline: 0519-83277346
Mr. Yao: 13813572798
Mr. Wang: 18861101169




